Experts Agree: Turbo Cancers are Caused by the Toxic mRNA COVID-19 Jabs
Updated
We are hearing the term “Turbo Cancer” more and more often. What does Turbo Cancer mean? The phrase, which is essentially a long-term effect of the COVID-19 jabs, describes the long list of aggressive cancers that are rising at a record pace in COVID-19-vaccinated individuals. These Turbo Cancers, most often resulting in rapid death, include but are not limited to Leukemia, colon cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, brain tumors, pancreatic cancers, and so on that grow undetected very, very rapidly, and present at a late stage. When asked by Del Bigtree, “How do these cancers get to such a late stage in often very young individuals without being recognized,” oncologist Dr. William Makis explained:
“I think it’s the rapid growth of the tumors, and they don’t seem to be causing symptoms, so they only present when the tumors are quite large already–they are pretty much stage four, stage three, stage four when they’re presenting. And some of these tumors can grow quite big. Some of these tumor masses can get 10 centimeters, even 15 centimeters. Oncologists are just shocked; they struggle to treat them. They don’t know what to do with these cancers. Even if they try to surgically excise them, thinking that the tumor hasn’t spread, they will find out the tumor has already spread after the surgery; it grows that quickly.”
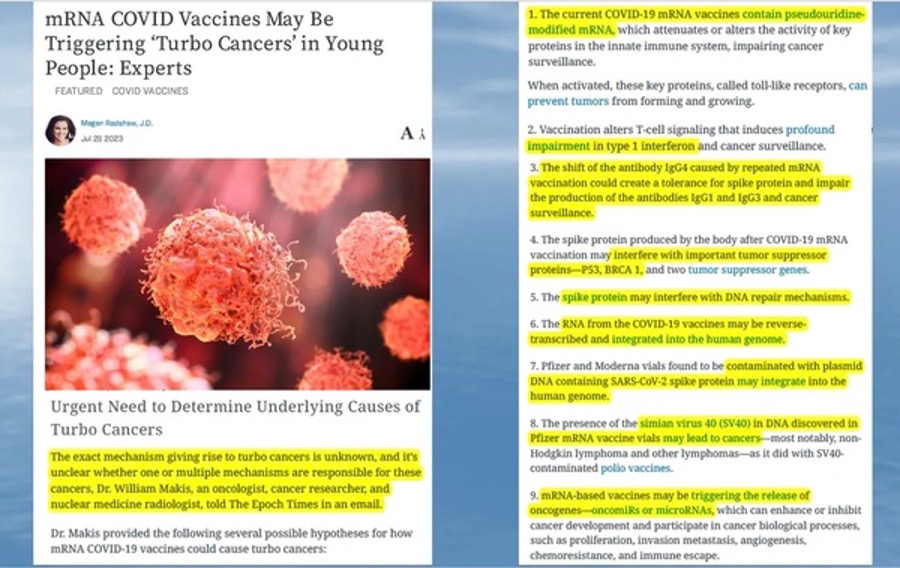
The Turbo Cancer crisis in the United States is already about as bad as can be imagined. Yet, unfortunately, it is becoming more lethal. What is causing these Turbo Cancers? Issuing grave warnings about the jabs throughout the pandemic, numerous esteemed doctors who have studied the unprecedented mRNA COVID-19 injections have all reached the same straightforward conclusion—ingredients in the toxic COVID-19 jabs damage the natural cancer surveillance system intrinsically provided by our body’s immune system.
Of course, the causes of the influx of Turbo Cancers are much more complex and complicated. Dr. Makis explained that a number of mechanisms have been proposed towards the cause and are starting to get backed by publications and findings in the literature. One significant explanation, also mentioned by Dr. Peter McCullough, is the ingredient N1-methyl-pseudouridine that is inserted into the mRNA. This ingredient—which won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2023—is added to keep the spike protein “alive” longer as it torments the entire body. Yet, in doing so, it alters the activity of critical proteins in the natural immune system, impairing the body’s ability to detect cancers. Typically, these vital proteins, called toll-like receptors, can prevent tumors from forming and growing, but not when pseudouridine-modified mRNA is around. A recent review published in PubMed titled “Review: N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ): Friend or foe of cancer” declared:
“Mounting evidence indicates that these vaccines, like many others, do not generate sterilizing immunity, leaving people vulnerable to recurrent infections. Additionally, it has been discovered that the mRNA vaccines inhibit essential immunological pathways, thus impairing early interferon signaling. Within the framework of COVID-19 vaccination, this inhibition ensures an appropriate spike protein synthesis and a reduced immune activation. Evidence is provided that adding 100% of N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ) to the mRNA vaccine in a melanoma model stimulated cancer growth and metastasis, while non-modified mRNA vaccines induced opposite results, thus suggesting that COVID-19 mRNA vaccines could aid cancer development.”
Read the last part of that last sentence again—mRNA vaccines could aid cancer development! Remarking on the PubMed review, authored by Rubio-Casillas et al., Dr. McCullough explained that not only could the COVID-19 mRNA jabs aid cancer development, but they could actually cause and worsen cancer, not make it better. And the more boosters one gets, the more maddening and accelerated the Turbo Cancer. Despite this unsettling evidence, the federal government continues to shake Big Pharma’s hand and simply looks the other way. Not even the American Cancer Society’s (ACS) recent warning of an unexplained surge in new aggressive cancers in the U.S. can spark the Biden administration to contemplate, “Hmmm… maybe we should take a really close look at these COVID-19 jabs.” It is maddening.
This is my father, who eagerly followed CDC guidance for full vaccination/boosters. Only pre existing condition is bicuspid aortic valve, no family cancer history. Was running 11k races into early 70s. Diagnosed Jan ‘24, he passed away earlier this month. It’s the shots. pic.twitter.com/4GcH7bKD1l
— PatriotMama 🇺🇸🪶🇺🇸 (@patriotmama30) April 17, 2024
Edward Dowd, author of Cause Unknown: The Epidemic of Sudden Death in 2021 & 2022, has reported for months that cancer statistics from the U.K. appear to support the Turbo Cancer claims in young people. Dowd noted a sharp uptick in cases of cancers in the under-45 age group that have already metastasized by the time they are diagnosed. Such cancers are known as “malignant neoplasms without specification of (the original) site (of excessive growth).” Dowd recently noted that, based on trends, cancer death rates should have gone down in 2021 and 2022, but they didn’t. Dowd shared, “We should have seen negative excess deaths, but we didn’t,” adding, “We saw add-ons and add-ons, and the absolute numbers are kind of stunning.”
Likewise, Professor Angus Dalgleish, an expert in immunology and Professor of Oncology at St. George’s Hospital Medical School in London, recently referenced the worthless boosters and their contribution to Turbo Cancer. He wrote on April 15 that “the third useless jab (booster) not only has no possible benefit” but shatters what is left of the immune response and controls cancers by suppressing the T cell responses and switching the antibody response to a tolerizing one. Hence, this completely destroys the immune response that had been regulating these underlying cancers. Dr. Makis also confirmed this belief, pointing out that vaccination alters T-cell signaling, causing profound impairment in type 1 interferon and cancer surveillance. According to Dalgleish, there is no worse candidate to stabilize the spike protein than N1-methyl-pseudouridine, noting it should have been avoided as [it] may cause excess cancer in recipients. And Makis and McCullough clearly agree. As he wrapped up his report, Dalgleish added:
“As I completed this last paragraph, I was informed by radio and by my GP surgery by email that our completely incompetent NHS and Department of Health are offering a spring booster campaign to those over 75 and at risk. What they will be at risk of is increasing their chances of dying of cancer. Do these people not read the literature, or are they just plain stupid, or just not care?”
Keep saying there is no such thing as turbo cancer. Shills.
Relying on semantics?
Late stage diagnosis of aggressive cancers are #turbocancers and it’s a common thing now thanks to LNP- modified mRNA injections.
Period! https://t.co/7Y2rj7fbPG— Dr. Lynn Fynn-derella🐭 (@Fynnderella1) April 18, 2024
As we watch the manifestation of Turbo Cancers here in the United States being swept under the rug, the obvious conclusion is the Biden administration and his tax-payer-funded agencies also “just don’t care.” But what they don’t realize is the fact we can’t be silenced. With much gratitude, Dr. Makis, Dr. McCullough, and several others have been sounding the alarm about Turbo Cancers since last fall. Still, finding information on the cancer tragedy—or any tragedy tied to the deadly jabs—is impossible in the deep state-controlled media arena. Nonetheless, despite being ignored by the likes of Google and most mainstream literature, Makis reported yesterday on X that six Turbo Cancer papers have come out in the past two weeks, bringing the total to roughly 26 papers —each documenting the ruin caused by Turbo Cancers. Additionally, Makis has relentlessly charted sudden deaths following the jabs throughout the pandemic. Together, these great leaders are bringing a much-needed focus on what is undoubtedly the most sinister global crime against humanity.